Force field (chemistry)
In the context of molecular modeling, a force field refers to the form and parameters of mathematical functions used to describe the potential energy of a system of particles (typically molecules and atoms). Force field functions and parameter sets are derived from both experimental work and high-level quantum mechanical calculations. "All-atom" force fields provide parameters for every type of atom in a system, including hydrogen, while "united-atom" force fields treat the hydrogen and carbon atoms in methyl and methylene groups as a single interaction center. "Coarse-grained" force fields, which are frequently used in long-time simulations of proteins, provide even more crude representations for increased computational efficiency.
The usage of the term "force field" in chemistry and computational biology differs from the standard usage in physics. In chemistry it is a system of potential energy functions rather than the gradient of a scalar potential, as defined in physics.
Functional form
The basic functional form of a force field encapsulates both bonded terms relating to atoms that are linked by covalent bonds, and nonbonded (also called "noncovalent") terms describing the long-range electrostatic and van der Waals forces. The specific decomposition of the terms depends on the force field, but a general form for the total energy in an additive force field can be written as 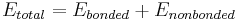 where the components of the covalent and noncovalent contributions are given by the following summations:
where the components of the covalent and noncovalent contributions are given by the following summations:
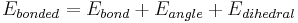
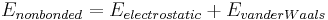
The bond and angle terms are usually modeled as harmonic oscillators in force fields that do not allow bond breaking. A more realistic description of a covalent bond at higher stretching is provided by the more expensive Morse potential. The functional form for the rest of the bonded terms is highly variable. Proper dihedral potentials are usually included. Additionally, "improper torsional" terms may be added to enforce the planarity of aromatic rings and other conjugated systems, and "cross-terms" that describe coupling of different internal variables, such as angles and bond lengths. Some force fields also include explicit terms for hydrogen bonds.
The nonbonded terms are most computationally intensive because they include many more interactions per atom. A popular choice is to limit interactions to pairwise energies. The van der Waals term is usually computed with a Lennard-Jones potential and the electrostatic term with Coulomb's law, although both can be buffered or scaled by a constant factor to account for electronic polarizability and produce better agreement with experimental observations.
Parameterization
In addition to the functional form of the potentials, a force field defines a set of parameters for each type of atom. For example, a force field would include distinct parameters for an oxygen atom in a carbonyl functional group and in a hydroxyl group. The typical parameter set includes values for atomic mass, van der Waals radius, and partial charge for individual atoms, and equilibrium values of bond lengths, bond angles, and dihedral angles for pairs, triplets, and quadruplets of bonded atoms, and values corresponding to the effective spring constant for each potential. Most current force fields use a "fixed-charge" model by which each atom is assigned a single value for the atomic charge that is not affected by the local electrostatic environment; proposed developments in next-generation force fields incorporate models for polarizability, in which a particle's charge is influenced by electrostatic interactions with its neighbors. For example, polarizability can be approximated by the introduction of induced dipoles; it can also be represented by Drude particles, or massless, charge-carrying virtual sites attached by a springlike harmonic potential to each polarizable atom. The introduction of polarizability into force fields in common use has been inhibited by the high computational expense associated with calculating the local electrostatic field.
Although many molecular simulations involve biological macromolecules such as proteins, DNA, and RNA, the parameters for given atom types are generally derived from observations on small organic molecules that are more tractable for experimental studies and quantum calculations. Different force fields can be derived from dissimilar types of experimental data, such as enthalpy of vaporization (OPLS), enthalpy of sublimation (CFF), dipole moments, or various spectroscopic parameters (CFF).
Parameter sets and functional forms are defined by force field developers to be self-consistent. Because the functional forms of the potential terms vary extensively between even closely related force fields (or successive versions of the same force field), the parameters from one force field should never be used in conjunction with the potential from another.
Deficiencies
All force fields are based on numerous approximations and derived from different types of experimental data. Therefore they are called empirical. Some existing force fields do not account for electronic polarization of the environment, an effect that can significantly reduce electrostatic interactions of partial atomic charges. This problem was addressed by developing “polarizable force fields” [1][2] or using macroscopic dielectric constant. However, application of a single value of dielectric constant is questionable in the highly heterogeneous environments of proteins or biological membranes, and the nature of the dielectric depends on the model used [3].
All types of van der Waals forces are also strongly environment-dependent, because these forces originate from interactions of induced and “instantaneous” dipoles (see Intermolecular force). The original Fritz London theory of these forces can only be applied in vacuum. A more general theory of van der Waals forces in condensed media was developed by A. D. McLachlan in 1963 (this theory includes the original London’s approach as a special case) [4]. The McLachlan theory predicts that van der Waals attractions in media are weaker than in vacuum and follow the "like dissolves like" rule, which means that different types of atoms interact more weakly than identical types of atoms.[5]. This is in contrast to “combinatorial rules” or Slater-Kirkwood equation applied for development of the classical force fields. The “combinatorial rules” state that interaction energy of two dissimilar atoms (e.g. C…N) is an average of the interaction energies of corresponding identical atom pairs (i.e. C…C and N…N). According to McLachlan theory, the interactions of particles in a media can even be completely repulsive, as observed for liquid helium [4]. The conclusions of McLachlan theory are supported by direct measurements of attraction forces between different materials (Hamaker constant), as explained by Jacob Israelachvili in his book "Intermolecular and surface forces". It was concluded that "the interaction between hydrocarbons across water is about 10% of that across vacuum" [4]. Such effects are unaccounted in the standard molecular mechanics.
Another round of criticism came from practical applications, such as protein structure refinement. It was noted that CASP participants did not try to refine their models to avoid "a central embarrassment of molecular mechanics, namely that energy minimization or molecular dynamics generally leads to a model that is less like the experimental structure".[6] Actually, the force fields have been successfully applied for protein structure refinement in different X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy applications, especially using program XPLOR [7]. However, such refinement is driven primarily by a set of experimental constraints, whereas the force fields serve merely to remove interatomic hindrances. The results of calculations are practically the same with rigid sphere potentials implemented in program DYANA [8] (calculations from NMR data), or with programs for crystallographic refinement that do not use any energy functions. The deficiencies of the force fields remain a major bottleneck in homology modeling of proteins [9]. Such situation gave rise to development of alternative empirical scoring functions specifically for ligand docking [10], protein folding [11][12][13], homology model refinement[14], computational protein design [15][16][17], and modeling of proteins in membranes [18].
There is also an opinion that molecular mechanics may operate with energy which is irrelevant to protein folding or ligand binding [19]. The parameters of typical force fields reproduce enthalpy of sublimation, i.e. energy of evaporation of molecular crystals. However, it was recognized that protein folding and ligand binding are thermodynamically very similar to crystallization, or liquid-solid transitions, because all these processes represent “freezing” of mobile molecules in condensed media [20][21][22]. Therefore, free energy changes during protein folding or ligand binding are expected to represent a combination of an energy similar to heat of fusion (energy absorbed during melting of molecular crystals), a conformational entropy contribution, and solvation free energy. The heat of fusion is significantly smaller than enthalpy of sublimation [4]. Hence, the potentials describing protein folding or ligand binding must be weaker than potentials in molecular mechanics. Indeed, the energies of H-bonds in proteins are ~ -1.5 kcal/mol when estimated from protein engineering or alpha helix to coil transition data [23][24], but the same energies estimated from sublimation enthalpy of molecular crystals were -4 to -6 kcal/mol [25]. The depths of modified Lennard-Jones potentials derived from protein engineering data were also smaller than in typical force fields and followed the “like dissolves like” rule, as predicted by McLachlan theory [19].
Future Perspectives
Molecular mechanics or force field was first introduced apparently independently by Hill and by Westheimer in 1949, primarily applied to organic chemistry to estimate properties such as strain energies among others. The functional form of the force field, focused in this article applied to biological systems, was established by Lifson in the 1960s. For over a half century, force fields have served us well, providing useful insights into and interpretation of biomolecular structure and function. Undoubtedly, it will continue to be widely used, thanks to its computational efficiency, while its reliability will continue to be improved. Yet, there are many well-known deficiencies as noted above. In addition, the number of energy terms used in a given force field cannot be uniquely determined and a highly redundant number of degrees of freedom are typically used. Consequently, the "parameters" in different force fields can be vastly different. Of course, the emphasis to incorporate polarization into the standard pair-wise potentials can be very useful; however, there is no unique way of treating polarization in molecular mechanics because it is of quantum mechanical origin.[26][27] Furthermore, often we are more interested in the properties derived from the dynamic dependence of the force field itself on molecular fluctuations.
One possibility is that the future development of force field ought to move beyond the current molecular mechanics approach, by using quantum mechanics explicitly to construct the force field. A number of the "polarizable force fields" listed below, such as density fitting and bond-polarization, already included some of the key ingredients towards this goal. The explicit polarization (X-Pol) method appears to have established the fundamental theoretical framework for a quantal force field; the next step is to develop the necessary parameters to achieve more accurate results than classical mechanics can offer.[26][27]
Popular force fields
Different force fields are designed for different purposes.
MM2 was developed by Norman Allinger primarily for conformational analysis of hydrocarbons and other small organic molecules. It is designed to reproduce the equilibrium covalent geometry of molecules as precisely as possible. It implements a large set of parameters that is continuously refined and updated for many different classes of organic compounds (MM3 and MM4).[28][29][30][31][32]
CFF was developed by Warshel, Lifson and coworkers as a general method for unifying studies of energies, structures and vibration of general molecules and molecular crystals. The CFF program, developed by Levitt and Warshel, is based on the Cartesian representation of all the atoms, and it served as the basis for many subsequent simulation programs.
ECEPP was developed specifically for modeling of peptides and proteins. It uses fixed geometries of amino acid residues to simplify the potential energy surface. Thus, the energy minimization is conducted in the space of protein torsion angles. Both MM2 and ECEPP include potentials for H-bonds and torsion potentials for describing rotations around single bonds. ECEPP/3 was implemented (with some modifications) in Internal Coordinate Mechanics and FANTOM [33].
AMBER, CHARMM and GROMOS have been developed primarily for molecular dynamics of macromolecules, although they are also commonly applied for energy minimization. Therefore, the coordinates of all atoms are considered as free variables.
Classical force fields
- AMBER (Assisted Model Building and Energy Refinement) - widely used for proteins and DNA.
- CHARMM (Chemistry at HARvard Molecular Mechanics) - originally developed at Harvard, widely used for both small molecules and macromolecules
- CHARMm - commercial version of CHARMM, available through Accelrys.
- CVFF - also broadly used for small molecules and macromolecules.
- COSMOS-NMR - hybrid QM/MM forcefield adapted to a variety of inorganic compounds, organic compounds and biological macromolecules, including semi-empirical calculation of atomic charges and NMR properties. COSMOS-NMR is optimized for NMR based structure elucidation and implemented in COSMOS molecular modelling package.[34]
- GROMACS - the force field optimized for the molecular dynamics package of the same name.
- GROMOS - a force field that comes as part of the GROMOS (GROningen MOlecular Simulation package), a general-purpose molecular dynamics computer simulation package for the study of biomolecular systems. GROMOS force field (A-version) has been developed for application to aqueous or apolar solutions of proteins, nucleotides and sugars. However, a gas phase version (B-version) for simulation of isolated molecules is also available.
- OPLS (Optimized Potential for Liquid Simulations) (variations include OPLS-AA, OPLS-UA, OPLS-2001, OPLS-2005) - developed by William L. Jorgensen at the Yale University Department of Chemistry.
- ENZYMIX – a general polarizable force field for modeling chemical reactions in biological molecules. This force field is implemented with the empirical valence bond (EVB) method and is also combined with the semimacroscopic PDLD approach in the program in the MOLARIS package.
- ECEPP/2 - first force field for polypeptide molecules - developed by F.A. Momany, H.A. Scheraga and colleagues.
- QCFF/PI – A general force field for conjugated molecules.[35].[36]
- UFF - A general force field with parameters for the full periodic table up to and including the actinoids - developed at Colorado State University.[37]
Second-generation force fields
- CFF - a family of forcefields adapted to a broad variety of organic compounds, includes force fields for polymers, metals, etc.
- MMFF (Merck Molecular Force Field)- developed at Merck, for a broad range of molecules.
- MM2, MM3, MM4 - developed by Norman Allinger, parametrized for a broad range of molecules.
- QVBMM - developed by Vernon G. S. Box, parameterized for all biomolecules and a broad range of organic molecules, and implemented in StruMM3D (STR3DI32).
Polarizable force fields based on electronic structural theory
- X-Pol: the Explicit Polarization Theory[1][26][27] - a fragment-based electronic structure method introduced by Jiali Gao [2] at the University of Minnesota, which can be used at any level of theory—ab initio Hartree-Fock (HF), semiempirical molecular orbital theory, correlated wave function theory, or Kohn-Sham (KS) density functional theory (DFT). It is capable of performing more than 3200 steps (3.2 ps) of MD simulations of a fully solvated protein in water with periodic boundary conditions, consisting of about 15000 atoms and 30000 basis functions on a single processor in 24 hours in 2008, with a full quantum mechanical representation of the entire system.[38] Note that the first MD simulation of a protein by Gelin, McCammon and Karplus in 1979 lasted just over 9 ps using a United-Atom force field without solvent.
Polarizable force field based on induced dipole
- CFF/ind and ENZYMIX – The first polarizable force field [39] which has subsequently been used in many applications to biological systems.[2].
- DRF90 developed by P. Th. van Duijnen and coworkers.
- PIPF – The polarizable intermolecular potential for fluids is an induced point-dipole force field for organic liquids and biopolymers. The molecular polarization is based on Thole's interacting dipole (TID) model and was developed by Jiali Gao [3] at the University of Minnesota.[40][41]
Polarizable force fields based on point charges
- PFF (Polarizable Force Field) developed by Richard A. Friesner and coworkers.
- SP-basis Chemical Potential Equalization (CPE) approach developed by R. Chelli and P. Procacci.
- CHARMM polarizable force field developed by S. Patel (University of Delaware) and C. L. Brooks III (University of Michigan).
- AMBER polarizable force field developed by Jim Caldwell and coworkers.
- CHARMM polarizable force field based on the classical Drude oscillator developed by A. MacKerell (University of Maryland, Baltimore) and B. Roux (University of Chicago).[42][43]
Polarizable force fields based on distributed multipoles
- The SIBFA (Sum of Interactions Between Fragments Ab initio computed) force field [44] for small molecules and flexible proteins, developed by Nohad Gresh (Paris V, René Descartes University) and Jean-Philip Piquemal (Paris VI, Pierre & Marie Curie University). SIBFA is a molecular mechanics procedure formulated and calibrated on the basis of ab initio supermolecule computations. Its purpose is to enable the simultaneous and reliable computations of both intermolecular and conformational energies governing the binding specificities of biologically and pharmacologically relevant molecules. This procedure enables an accurate treatment of transition metals. The inclusion of a ligand field contribution allows computations on "open-shell" metalloproteins.
- AMOEBA (Atomic Multipole Optimized Energetics for Biomolecular Applications) force field developed by Pengyu Ren (University of Texas at Austin) and Jay W. Ponder (Washington University).
- ORIENT procedure developed by Anthony J. Stone (Cambridge University) and coworkers.
- Non-Empirical Molecular Orbital (NEMO) procedure developed by Gunnar Karlström and coworkers at Lund University (Sweden)[45]
Polarizable force fields based on density
- Gaussian Electrostatic Model (GEM)[44][46][47] - a polarizable force field based on Density Fitting developed by Thomas A. Darden and G. Andrés Cisneros at NIEHS; and Jean-Philip Piquemal (Paris VI University).
- Polarizable procedure based on the Kim-Gordon approach developed by Jürg Hutter and coworkers (University of Zürich)
Polarizable force fields based on Bond Polarization Theory (BPT)
- COSMOS-NMR (Computer Simulation of Molecular Structure) - developed by Ulrich Sternberg and coworkers. Hybrid QM/MM force field enables explicit quantum-mechanical calculation of electrostatic properties using localized bond orbitals with fast BPT formalism.[48] Atomic charge fluctuation is possible in each molecular dynamics step.
Reactive force fields
- ReaxFF - reactive force field developed by Adri van Duin, William Goddard and coworkers. It is fast, transferable and is the computational method of choice for atomistic-scale dynamical simulations of chemical reactions.
- EVB (empirical valence bond) - this reactive force field, introduced by Warshel and coworkers, is probably the most reliable and physically consistent way of using force fields in modeling chemical reactions in different environments. The EVB facilitates calculations of actual activation free energies in condensed phases and in enzymes.
- RWFF - reactive force field for water developed by Detlef W. M. Hofmann, Liudmila N. Kuleshova and Bruno D'Aguanno. It is very fast, reproduces the experimental data of neutron scattering accurately, and allows the simulation of bond formation/breaking of water and acids.[49]
Coarse-grained force fields
- VAMM (Virtual atom molecular mechanics) - a coarse-grained force field developed by Korkut and Hendrickson for molecular mechanics calculations such as large scale conformational transitions based on the virtual interactions of C-alpha atoms. It is a knowledge based force field and formulated to capture features dependent on secondary structure and on residue-specific contact information in proteins.[50]
Other
- VALBOND - a function for angle bending that is based on valence bond theory and works for large angular distortions, hypervalent molecules, and transition metal complexes. It can be incorporated into other force fields such as CHARMM and UFF.
Water models
The set of parameters used to model water or aqueous solutions (basically a force field for water) is called a water model. Water has attracted a great deal of attention due to its unusual properties and its importance as a solvent. Many water models have been proposed; some examples are TIP3P, TIP4P, SPC, Flexible SPC, and ST2.
See also
References
- ^ Ponder JW and Case DA. (2003). "Force fields for protein simulations". Adv. Prot. Chem. 66 27-85.
- ^ a b Warshel A, Sharma PK, Kato M and Parson WW (2006). "Modeling Electrostatic Effects in Proteins." Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1764 1647-1676.
- ^ Schutz CN. and Warshel A. (2001). "What are the dielectric "constants" of proteins and how to validate electrostatic models?". Proteins 44 400-417.
- ^ a b c d Israelachvili, J.N. (1992). Intermolecular and surface forces. Academic Press, San Diego.
- ^ Leckband, D. and Israelachvili, J. (2001). "Intermolecular forces in biology". Quart. Rev. Biophys. 34 105-267.
- ^ Koehl P. and Levitt M. (1999). "A brighter future for protein structure prediction". Nature Struct. Biol. 6 108-111.
- ^ Brunger AT and Adams PD. (2002). "Molecular dynamics applied to X-ray structure refinement". Acc. Chem. Res. 35 404-412.
- ^ Guntert P. (1998). "Structure calculation of biological macromolecules from NMR data". Quart. Rev. Biophys. 31 145-237.
- ^ Tramontano A. and Morea V. (2003). "Assessment of homology-based predictions in CASP5". Proteins. 53 352-368.
- ^ Gohlke H. and Klebe G. (2002). "Approaches to the description and prediction of the binding affinity of small-molecule ligands to macromolecular receptors". Angew. Chem. Internat. Ed. 41 2644-2676.
- ^ Edgcomb S.P. and Murphy K.P. (2000). "Structural energetics of protein folding and binding". Current Op. Biotechnol. 11 62-66.
- ^ Lazaridis T. and Karplus M. (2000). "Effective energy functions for protein structure prediction". Curr. Op. Struct. Biol. 10 139-145.
- ^ Levitt M. and Warshel A. (1975). "Computer Simulations of Protein Folding". Nature 253 694-698.
- ^ Krieger E., Joo K., Lee J., Lee J., Raman S., Thompson J., Tyka M., Baker D. and Karplus K. (2009). "Improving physical realism, stereochemistry, and side-chain accuracy in homology modeling: Four approaches that performed well in CASP8". Proteins 77 Suppl 9 114-122.
- ^ Gordon DB, Marshall SA, and Mayo SL (1999). "Energy functions for protein design". Curr. Op. Struct. Biol. 9 509-513.
- ^ Mendes J., Guerois R, and Serrano L (2002). "Energy estimation in protein design". Curr. Op. Struct. Biol. 12 441-446.
- ^ Rohl CA, Strauss CEM, Misura KMS, and Baker D. (2004). "Protein structure prediction using Rosetta". Meth. Enz. 383 66-93.
- ^ Lomize AL, Pogozheva ID, Lomize MA, Mosberg HI (2006). "Positioning of proteins in membranes: A computational approach". Protein Sci. 15 1318-1333.
- ^ a b Lomize A.L., Reibarkh M.Y. and Pogozheva I.D. (2002). "Interatomic potentials and solvation parameters from protein engineering data for buried residues". Protein Sci. 11 1984-2000.
- ^ Murphy K.P. and Gill S.J. (1991). "Solid model compounds and the thermodynamics of protein unfolding". J. Mol. Biol. 222 699-709.
- ^ Shakhnovich, E.I. and Finkelstein, A.V. (1989). "Theory of cooperative transitions in protein molecules. I. Why denaturation of globular proteins is a first-order phase transition". Biopolymers 28 1667-1680.
- ^ Graziano, G., Catanzano, F., Del Vecchio, P., Giancola, C., and Barone, G. (1996). "Thermodynamic stability of globular proteins: a reliable model from small molecule studies". Gazetta Chim. Italiana 126 559-567.
- ^ Myers J.K. and Pace C.N. (1996). "Hydrogen bonding stabilizes globular proteins". Biophys. J. 71 2033-2039.
- ^ Scholtz J.M., Marqusee S., Baldwin R.L., York E.J., Stewart J.M., Santoro M., and Bolen D.W. (1991). "Calorimetric determination of the enthalpy change for the alpha-helix to coil transition of an alanine peptide in water". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88 2854-2858.
- ^ Gavezotti A. and Filippini G. (1994). "Geometry of intermolecular X-H...Y (X,Y=N,O) hydrogen bond and the calibration of empirical hydrogen-bond potentials". J. Phys. Chem. 98 4831-4837.
- ^ a b c Gao, J. (1997). "Toward a Molecular Orbital Derived Empirical Potential for Liquid Simulations". J. Phys. Chem. B 101 657-663.
- ^ a b c Xie, W., and Gao, J. (2007). "Design of a Next Generation Force Field: The X-POL Potential". J. Chem. Theory Comput. 3 1890-1900.
- ^ Allinger, Norman L. (1977). "Conformational analysis. 130. MM2. A hydrocarbon force field utilizing V1 and V2 torsional terms". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 99 8127-8134.
- ^ MM2 and MM3 home page
- ^ Allinger, N.L., Yuh, Y.H., & Lii, J-H. (1989). "Molecular Mechanics. The MM3 Force Field for Hydrocarbons. 1". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 111 8551-8565.
- ^ Lii, J-H., & Allinger, N.L. (1989). "Molecular Mechanics. The MM3 Force Field for Hydrocarbons. 2. Vibrational Frequencies and Thermodynamics". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 111 8566-8575.
- ^ Lii, J-H., & Allinger, N.L. (1989). "Molecular Mechanics. The MM3 Force Field for Hydrocarbons. 3. The van der Waals Potentials and Crystal data for Aliphatic and Aromatic Hydrocarbons". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 111 8576-8582.
- ^ Schaumann, T., Braun, W. and Wutrich, K. (1990). "The program FANTOM for energy refinement of polypeptides and proteins using a Newton-Raphson minimizer in torsion angle space". Biopolymers 29 679-694.
- ^ Möllhoff, Margit and Sternberg, Ulrich (2001). "Molecular Mechanics with fluctuating atomic charges - a new force field with semi-empirical charge calculation". J. Mol. Model. 7 90-102.
- ^ Warshel, A. (1973). "Quantum Mechanical Consistent Force Field (QCFF/PI) Method: Calculations of Energies, Conformations and Vibronic Interactions of Ground and Excited States of Conjugated Molecules" Israel J. Chem. 11 709.
- ^ Warshel, A. and Levitt, M. (1974). "QCFF/PI: A Program for the Consistent Force Field Evaluation of Equilibrium Geometries and Vibrational Frequencies of Molecules". QCPE 247, Quantum Chemistry Program Exchange, Indiana University.
- ^ Rappé, A.K. et al. (1992). "UFF, a Full Periodic Table Force Field for Molecular Mechanics and Molecular Dynamics Simulations" J. Am. Chem. Soc. 114 10024-10035.
- ^ Xie, W., Orozco, M., Truhlar, D. G., and Gao, J. (2009) "X-Pol Potential: An Electronic Structure-Based Force Field for Molecular Dynamics Simulation of a Solvated Protein in Water". J. Chem. Theory Comput. 5 459-467.
- ^ Warshel A. and Levitt M. (1976) "Theoretical Studies of Enzymatic Reactions: Dielectric Electrostatic and Steric Stabilization of the Carbonium Ion in the Reaction of Lysozyme". J. Mol. Biol. 103 227-249.
- ^ Gao, J., Habibollahzadeh, D., and Shao, L. (1995) "A Polarizable Intermolecular Potential Functions for Simulations of Liquid Alcohols". J. Phys. Chem. 99 16460-16467.
- ^ Xie, W., Pu, J., MacKerell, A. D., Jr., and Gao, J. (2007) "Development of a Polarizable Intermolecular Potential Function (PIPF) for Liquid Amides and Alkanes". J. Chem. Theory Comput. 3 1878-1889.
- ^ Anisimov, V.M., Lamoureux, G., Vorobyov, I.V., Huang, N., Roux, B. and MacKerell, A.D., Jr. (2005) "Determination of Electrostatic Parameters for a Polarizable Force Field Based on the Classical Drude Oscillator". J. Chem. Theory Comput. 1 153-168.
- ^ Yu, H., Whitfield, T.W., Harder, E., Lamoureux, G., Vorobyov, I., Anisimov, V. M., MacKerell, A.D., Jr., and Roux, B. (2010) "Simulating Monovalent and Divalent Ions in Aqueous Solution Using a Drude Polarizable Force Field". J. Chem. Theory Comput. 6 774–786.
- ^ a b Gresh, N., Cisneros, G. A., Darden, T. A. and Piquemal, J-P. (2007) "Anisotropic, polarizable molecular mechanics studies of inter-, intra-molecular interactions, and ligand-macromolecule complexes. A bottom-up strategy." J. Chem. Theory. Comput. 3 1960.
- ^ O. Engkvist, P.-O. Åstrand, and G. Karlström. "Accurate intermolecular potentials obtained from molecular wave funcions: Bridging the gap between quantum chemistry and molecular simulations". Chem. Rev., 100:4087-4108, 2000.
- ^ Piquemal, J-P, Cisneros, G.A., Reinhardt, P., Gresh, N. and Darden, T.A. (2006). "Towards a Force Field based on Density Fitting". J. Chem. Phys. 124 104101.
- ^ Cisneros, G.A., Piquemal, J-P and Darden, T.A. (2006). "Generalization of the Gaussian Electrostatic Model: extension to arbitrary angular momentum, distributed multipoles and speedup with reciprocal space methods". J. Chem. Phys. 125 184101.
- ^ Sternberg, Ulrich, Koch, Frank-Thomas and Möllhoff, Margit (1994). "New Approach to the Semiempirical Calculation of Atomic Charges for Polypeptides and Large Molecular Systems" J. Comp. Chem. 15 524-531.
- ^ D.W.M. Hofmann, L. N. Kuleshova, B. D'Aguanno (2007). "A new reactive potential for the Molecular Dynamics simulation of liquid water". Chem.Phys.Lett. 448 138-143.
- ^ A. Korkut, W.A. Hendrickson (2009). "A force field for virtual atom molecular mechanics of proteins." Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106 15667–15672.
Further reading
- Schlick T. (2000). Molecular Modeling and Simulation: An Interdisciplinary Guide Interdisciplinary Applied Mathematics: Mathematical Biology. Springer-Verlag New York, NY.
- Israelachvili, J.N. (1992) Intermolecular and surface forces. Academic Press, San Diego.
- Warshel A (1991). "Computer Modeling of Chemical Reactions in Enzymes and Solutions" John Wiley & Sons New York.